When referring to the compilation of Henry's Law Constants, please cite
this publication:
R. Sander: Compilation of Henry's law constants (version 5.0.0) for
water as solvent, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 23, 10901-12440 (2023),
doi:10.5194/acp-23-10901-2023
The publication from 2023 replaces that from 2015,
which is now obsolete. Please do not cite the old paper anymore.
|
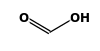
| FORMULA: | HCOOH |
|
TRIVIAL NAME:
|
formic acid
|
|
CAS RN: | 64-18-6 |
STRUCTURE
(FROM
NIST):
|
|
|
InChIKey: | BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|
|
References |
Type |
Notes |
| [mol/(m3Pa)] |
[K] |
|
|
|
| 8.8×101 |
6100 |
Burkholder et al. (2019) |
L |
|
| 8.8×101 |
6100 |
Burkholder et al. (2015) |
L |
|
| 8.8×101 |
6100 |
Sander et al. (2011) |
L |
|
| 8.8×101 |
6100 |
Sander et al. (2006) |
L |
|
| 6.7×101 |
5900 |
Staudinger and Roberts (2001) |
L |
|
| 8.8×101 |
6100 |
Johnson et al. (1996) |
M |
|
| 5.4×101 |
|
Khan et al. (1995) |
M |
|
| 5.4×101 |
5600 |
Khan and Brimblecombe (1992) |
M |
|
| 1.3×102 |
|
Servant et al. (1991) |
M |
489)
|
| 7.3×101 |
|
Johnson (1990) |
M |
80)
|
| 1.5×101 |
|
Hwang et al. (1992) |
V |
|
|
5700 |
Abraham (1984) |
V |
|
|
5600 |
Abraham (1984) |
R |
490)
|
|
5700 |
Winiwarter et al. (1988) |
T |
491)
|
| 3.7×101 |
5700 |
Jacob (1986) |
T |
492)
|
| 5.5×101 |
|
Keene and Galloway (1986) |
T |
|
| 5.9×101 |
|
Gaffney and Senum (1984) |
X |
391)
493)
|
| 5.1×101 |
|
Johnson et al. (1996) |
C |
|
| 5.1×101 |
|
Keene et al. (1995) |
C |
|
| 5.3×101 |
|
Keene et al. (1995) |
C |
|
| 3.7×101 |
5700 |
Lelieveld and Crutzen (1991) |
C |
|
| 3.5×101 |
5700 |
Pandis and Seinfeld (1989) |
C |
|
| 2.1×102 |
|
Keshavarz et al. (2022) |
Q |
|
| 4.0×101 |
|
Duchowicz et al. (2020) |
Q |
185)
|
| 2.2×101 |
|
Wang et al. (2017) |
Q |
81)
239)
|
| 2.5×102 |
|
Wang et al. (2017) |
Q |
81)
240)
|
| 1.0×102 |
|
Wang et al. (2017) |
Q |
81)
241)
|
| 2.3×102 |
|
Hilal et al. (2008) |
Q |
|
| 1.2×101 |
|
Modarresi et al. (2007) |
Q |
68)
|
|
5800 |
Kühne et al. (2005) |
Q |
|
| 5.8×101 |
|
Yaffe et al. (2003) |
Q |
249)
250)
|
| 8.6×101 |
|
Abraham (2003) |
Q |
|
| 7.7 |
|
Katritzky et al. (1998) |
Q |
|
| 5.9×101 |
|
Duchowicz et al. (2020) |
? |
21)
186)
|
|
6500 |
Kühne et al. (2005) |
? |
|
| 1.3×101 |
|
Yaws (1999) |
? |
21)
|
| 8.9 |
|
Yaws and Yang (1992) |
? |
21)
|
Data
The first column contains Henry's law solubility constant
at the reference temperature of 298.15 K.
The second column contains the temperature dependence
, also at the
reference temperature.
References
-
Abraham, M. H.: Thermodynamics of solution of homologous series of solutes in water, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1, 80, 153–181, doi:10.1039/F19848000153 (1984).
-
Abraham, M. H.: The determination of air/water partition coefficients for alkyl carboxylic acids by a new indirect method, J. Environ. Monit., 5, 747–752, doi:10.1039/B308175C (2003).
-
Burkholder, J. B., Sander, S. P., Abbatt, J., Barker, J. R., Huie, R. E., Kolb, C. E., Kurylo, M. J., Orkin, V. L., Wilmouth, D. M., & Wine, P. H.: Chemical Kinetics and Photochemical Data for Use in Atmospheric Studies, Evaluation No. 18, JPL Publication 15-10, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, URL https://jpldataeval.jpl.nasa.gov (2015).
-
Burkholder, J. B., Sander, S. P., Abbatt, J., Barker, J. R., Cappa, C., Crounse, J. D., Dibble, T. S., Huie, R. E., Kolb, C. E., Kurylo, M. J., Orkin, V. L., Percival, C. J., Wilmouth, D. M., & Wine, P. H.: Chemical Kinetics and Photochemical Data for Use in Atmospheric Studies, Evaluation No. 19, JPL Publication 19-5, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, URL https://jpldataeval.jpl.nasa.gov (2019).
-
Duchowicz, P. R., Aranda, J. F., Bacelo, D. E., & Fioressi, S. E.: QSPR study of the Henry’s law constant for heterogeneous compounds, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 154, 115–121, doi:10.1016/J.CHERD.2019.12.009 (2020).
-
Gaffney, J. S. & Senum, G. I.: Peroxides, peracids, aldehydes, and PANs and their links to natural and anthropogenic organic sources, in: Gas-Liquid Chemistry of Natural Waters, edited by Newman, L., pp. 5–1–5–7, NTIS TIC-4500, UC-11, BNL 51757 Brookhaven National Laboratory (1984).
-
Hilal, S. H., Ayyampalayam, S. N., & Carreira, L. A.: Air-liquid partition coefficient for a diverse set of organic compounds: Henry’s law constant in water and hexadecane, Environ. Sci. Technol., 42, 9231–9236, doi:10.1021/ES8005783 (2008).
-
Hwang, Y.-L., Olson, J. D., & Keller, II, G. E.: Steam stripping for removal of organic pollutants from water. 2. Vapor-liquid equilibrium data, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 31, 1759–1768, doi:10.1021/IE00007A022 (1992).
-
Jacob, D. J.: Chemistry of OH in remote clouds and its role in the production of formic acid and peroxymonosulfate, J. Geophys. Res., 91, 9807–9826, doi:10.1029/JD091ID09P09807 (1986).
-
Johnson, B. J.: The carbon isotope content and concentration of ambient formic acid and acetic acid, Ph.D. thesis, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, URL https://hdl.handle.net/10150/185355 (1990).
-
Johnson, B. J., Betterton, E. A., & Craig, D.: Henry’s law coefficients of formic and acetic acids, J. Atmos. Chem., 24, 113–119, doi:10.1007/BF00162406 (1996).
-
Katritzky, A. R., Wang, Y., Sild, S., Tamm, T., & Karelson, M.: QSPR studies on vapor pressure, aqueous solubility, and the prediction of water-air partition coefficients, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 38, 720–725, doi:10.1021/CI980022T (1998).
-
Keene, W. C. & Galloway, J. N.: Considerations regarding sources for formic and acetic acids in the troposphere, J. Geophys. Res., 91, 14 466–14 474, doi:10.1029/JD091ID13P14466 (1986).
-
Keene, W. C., Mosher, B. W., Jacob, D. J., Munger, J. W., Talbot, R. W., Artz, R. S., Maben, J. R., Daube, B. C., & Galloway, J. N.: Carboxylic acids in a high-elevation forested site in central Virginia, J. Geophys. Res., 100, 9345–9357, doi:10.1029/94JD01247 (1995).
-
Keshavarz, M. H., Rezaei, M., & Hosseini, S. H.: A simple approach for prediction of Henry’s law constant of pesticides, solvents, aromatic hydrocarbons, and persistent pollutants without using complex computer codes and descriptors, Process Saf. Environ. Prot., 162, 867–877, doi:10.1016/J.PSEP.2022.04.045 (2022).
-
Khan, I. & Brimblecombe, P.: Henry’s law constants of low molecular weight (<130) organic acids, J. Aerosol Sci., 23, S897–S900, doi:10.1016/0021-8502(92)90556-B (1992).
-
Khan, I., Brimblecombe, P., & Clegg, S. L.: Solubilities of pyruvic acid and the lower (C1-C6) carboxylic acids. Experimental determination of equilibrium vapour pressures above pure aqueous and salt solutions, J. Atmos. Chem., 22, 285–302, doi:10.1007/BF00696639 (1995).
-
Kühne, R., Ebert, R.-U., & Schüürmann, G.: Prediction of the temperature dependency of Henry’s law constant from chemical structure, Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, 6705–6711, doi:10.1021/ES050527H (2005).
-
Lelieveld, J. & Crutzen, P. J.: The role of clouds in tropospheric photochemistry, J. Atmos. Chem., 12, 229–267, doi:10.1007/BF00048075 (1991).
-
Modarresi, H., Modarress, H., & Dearden, J. C.: QSPR model of Henry’s law constant for a diverse set of organic chemicals based on genetic algorithm-radial basis function network approach, Chemosphere, 66, 2067–2076, doi:10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2006.09.049 (2007).
-
Pandis, S. N. & Seinfeld, J. H.: Sensitivity analysis of a chemical mechanism for aqueous-phase atmospheric chemistry, J. Geophys. Res., 94, 1105–1126, doi:10.1029/JD094ID01P01105 (1989).
-
Sander, S. P., Friedl, R. R., Golden, D. M., Kurylo, M. J., Moortgat, G. K., Keller-Rudek, H., Wine, P. H., Ravishankara, A. R., Kolb, C. E., Molina, M. J., Finlayson-Pitts, B. J., Huie, R. E., & Orkin, V. L.: Chemical Kinetics and Photochemical Data for Use in Atmospheric Studies, Evaluation Number 15, JPL Publication 06-2, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA, URL https://jpldataeval.jpl.nasa.gov (2006).
-
Sander, S. P., Abbatt, J., Barker, J. R., Burkholder, J. B., Friedl, R. R., Golden, D. M., Huie, R. E., Kolb, C. E., Kurylo, M. J., Moortgat, G. K., Orkin, V. L., & Wine, P. H.: Chemical Kinetics and Photochemical Data for Use in Atmospheric Studies, Evaluation No. 17, JPL Publication 10-6, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, URL https://jpldataeval.jpl.nasa.gov (2011).
-
Servant, J., Kouadio, G., Cros, B., & Delmas, R.: Carboxylic monoacids in the air of Mayombe forest (Congo): Role of the forest as a source or sink, J. Atmos. Chem., 12, 367–380, doi:10.1007/BF00114774 (1991).
-
Staudinger, J. & Roberts, P. V.: A critical compilation of Henry’s law constant temperature dependence relations for organic compounds in dilute aqueous solutions, Chemosphere, 44, 561–576, doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00505-1 (2001).
-
Wang, C., Yuan, T., Wood, S. A., Goss, K.-U., Li, J., Ying, Q., & Wania, F.: Uncertain Henry’s law constants compromise equilibrium partitioning calculations of atmospheric oxidation products, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 17, 7529–7540, doi:10.5194/ACP-17-7529-2017 (2017).
-
Winiwarter, W., Puxbaum, H., Fuzzi, S., Facchini, M. C., Orsi, G., Beltz, N., Enderle, K.-H., & Jaeschke, W.: Organic acid gas and liquid-phase measurements in Po valley fall-winter conditions in the presence of fog, Tellus, 40B, 348–357, doi:10.1111/J.1600-0889.1988.TB00109.X (1988).
-
Yaffe, D., Cohen, Y., Espinosa, G., Arenas, A., & Giralt, F.: A fuzzy ARTMAP-based quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR) for the Henry’s law constant of organic compounds, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 43, 85–112, doi:10.1021/CI025561J (2003).
-
Yaws, C. L.: Chemical Properties Handbook, McGraw-Hill, Inc., ISBN 0070734011 (1999).
-
Yaws, C. L. & Yang, H.-C.: Henry’s law constant for compound in water, in: Thermodynamic and Physical Property Data, edited by Yaws, C. L., pp. 181–206, Gulf Publishing Company, Houston, TX, ISBN 0884150313 (1992).
Type
Table entries are sorted according to reliability of the data, listing
the most reliable type first: L) literature review, M) measured, V)
VP/AS = vapor pressure/aqueous solubility, R) recalculation, T)
thermodynamical calculation, X) original paper not available, C)
citation, Q) QSPR, E) estimate, ?) unknown, W) wrong. See Section 3.1
of Sander (2023) for further details.
Notes
| 21) |
Several references are given in the list of Henry's law constants but not assigned to specific species. |
| 68) |
Modarresi et al. (2007) use different descriptors for their calculations. They conclude that a genetic algorithm/radial basis function network (GA/RBFN) is the best QSPR model. Only these results are shown here. |
| 80) |
Value at T = 297 K. |
| 81) |
Value at T = 288 K. |
| 185) |
Value from the validation set for checking whether the model is satisfactory for compounds that are absent from the training set. |
| 186) |
Experimental value, extracted from HENRYWIN. |
| 239) |
Calculated using linear free energy relationships (LFERs). |
| 240) |
Calculated using SPARC Performs Automated Reasoning in Chemistry (SPARC). |
| 241) |
Calculated using COSMOtherm. |
| 249) |
Yaffe et al. (2003) present QSPR results calculated with the fuzzy ARTMAP (FAM) and with the back-propagation (BK-Pr) method. They conclude that FAM is better. Only the FAM results are shown here. |
| 250) |
Value from the training set. |
| 391) |
Value given here as quoted by Gaffney et al. (1987). |
| 489) |
The value given here was measured at a liquid-phase mixing ratio of 1 μmol mol−1. Servant et al. (1991) found that the Henry's law constant changes at higher concentrations. |
| 490) |
Abraham (1984) smoothed the values from a plot of enthalpy against carbon number. |
| 491) |
The value of Hs⊖ was taken from Keene and Galloway (1986). |
| 492) |
Calculated using thermodynamic data from Latimer (1952). |
| 493) |
Value at pH = 4. |
The numbers of the notes are the same as
in Sander (2023). References cited in the notes can be
found here.
|
* * *
Search Henry's Law Database
* * *
Convert Henry's Law Constants
* * *
|

